Financial Aid
Lesson Summary and Objectives
This lesson will teach you the fundamentals of financial aid including what it is and how to apply. This lesson will cover the following types of financial aid available to students interested in continuing their education after high school:
- Grants
- Scholarships
- Work-Study
- Loans
This lesson will discuss the differences between Federal, State, Institutional and Private Aid. Additionally, this lesson includes an activity in which students will calculate the tuition cost for the College of Southern Nevada (CSN), Nevada State College (NSC), University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV) and University of Nevada, Reno (UNR) to understand tuition fees and how financial aid impacts the overall cost of attendance.
Objective One
Learn about the four types of financial aid available to help students make the most informed financial investment in their future.
Objective Two
Assist all students regardless of citizenship status or academic standing in understanding how to apply for financial aid and maximize their aid potential.
Objective Three
Provide financial aid resources to help students complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) or apply to other financial aid.
Before you get started…
Financial Aid Fundamentals
For many students, applying for financial aid can seem like a complicated process but it doesn’t have to be! First, let’s go over what financial aid is, the different types of aid available to you and how to apply.
Financial Aid is money given or loaned to help pay for college or trade schools after you graduate high school.
The Types of Financial Aid
Grants
A sum of $ given to students to use towards school that does NOT need to be paid back. Think of grants as “free money” much like a scholarship.
Scholarships
A sum of $ given to students to use towards school that does NOT need to be paid back. Think of scholarships as “free money” much like a grant.
Work-Study
A program where college students can earn $ to pay for school or other expenses through part time jobs on campus. If you are interested make sure to speak to a financial aid counselor on campus to ask how to apply!
Loans
A sum of $ loaned to students to use towards school that MUST be paid back. Usually with interest!
Grants & Scholarships
=
Free $ You Keep
Loans
=
Borrowed $ You Pay Back
Work-Study
=
$ You Earn
The Sources of Financial Aid
| Type of Financial Aid | Source | Examples | Available to Undocumented Students |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Aid | Federal Government | Federal Pell Grant, Federal Student Loans, Parent PLUS Loan | No |
| State Aid | State Government | Nevada State Aid: Guinn Millennium Scholarship Nevada Promise Scholarship Silver State Opportunity Grant | Yes in NV (other states may vary) |
| Institutional Aid | Colleges and Universities | Examples: NSC Scorpion Scholarships UNLV Tuition + Award Program UNR Presidential Scholarship | Yes |
| Private Aid | Private organizations, businesses, and individuals | The Public Education Foundation The Cardenas Family Foundation A Seat at Our Table Scholarship The Dream National Scholarship | Yes |
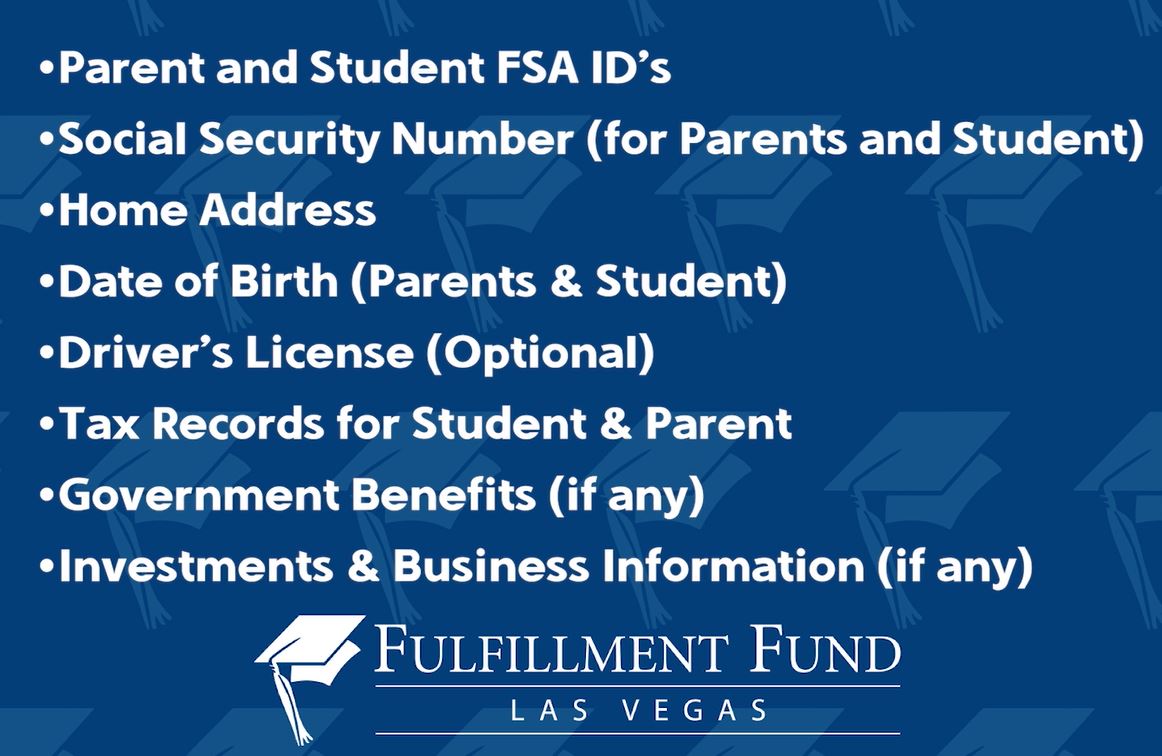
How to Apply for Financial Aid
Federal
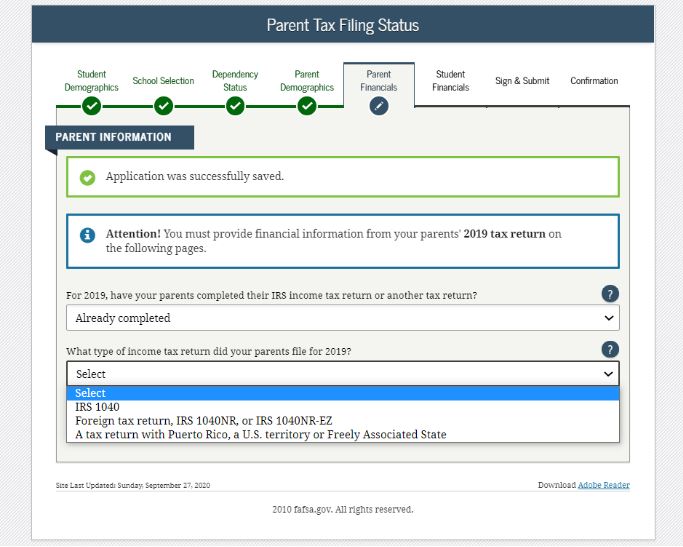
Complete and submit the FAFSA. Once submitted you will receive a Student Aid Report outlining all the federal aid you are eligible to receive. Check out our step-by-step video series on how to complete the FAFSA below!
Undocumented students: Ask the Financial Aid Office at your institution about an Alternative Needs Form or Institutional Methodology Form for you to submit instead of the FAFSA.
State
The State of Nevada awards high achieving students who graduate from high school and go on to pursue a higher education in state via the Governor Guinn Millennium Scholarship (GGMS) Program. Students are automatically considered for the scholarship upon high school graduation. Therefore, there is no application process.
To qualify, students must meet the following requirements:
- Graduate from a Nevada high school diploma with at least a 3.25 GPA (weighted or unweighted) OR a qualifying test score (1070 on the SAT or 21 on the ACT)
- Complete the following core curriculum: 4 units in English, 4 units in Math (including Algebra II or higher), 3 units in Science, 3 units in Social Science or History
- Be a Nevada resident for at least two years of their high school career
Students must be enrolled in at least 9 semester credits at an eligible community college or 12 semester credits at a state college or university to receive scholarship funding.
If you qualify for this scholarship, you will receive an award letter by mail after graduation (make sure your mailing address is updated with CCSD).
Students interested in attending CSN or another community college in Nevada can also apply to the Nevada Promise Scholarship to help pay for school!
The Silver State Opportunity Grant is another financial aid program offered by the state. Students must complete and submit the FAFSA to find out if they are eligible. If you are, you will be notified on your financial aid award letter.
Institutional
Colleges and universities offer their own financial aid that is awarded based on merit or need. Search each institution’s website or ask an admissions representative for scholarships opportunities. In addition, list each institution you have applied to when completing the FAFSA.
Private
Financial aid offered by private sources is usually awarded in the form of a scholarship. Research and apply for scholarship opportunities well before high school graduation.
Complete the FAFSA
Cost of Tuition and Attendance
Calculating the cost of tuition is an important step in the college-going process as it helps students understand tuition fees and how financial aid impacts the overall cost of attendance.
First, students must breakdown tuition fees. There are several types of fees (e.g., registration fees, technology fees, student services fees). Some fees are per credit, others may be per semester or a one-time fee at enrollment. If the fee states “per credit” students must multiply the fee amount per the number of credits taken. For example, $60 per credit for 15 credits will equal $900.
Once the cost of tuition is assessed, students can deduct any expected financial aid to determine the cost of attendance at an institution.

Financial aid is money given or loaned to help students pay for college or trade school. Financial aid is offered according to merit or need in the form of grants, scholarships, work-study, and loans.
Students may be required to maintain a minimum GPA or good academic standing to receive financial aid each semester. These requirements allow students to achieve Satisfactory Academic Progress (SAP). If a student does not meet SAP, they may lose their financial aid which means paying for tuition out of pocket. SAP requirements can be found on each institution’s financial aid web page.
Students must also be considered “full time” in order to receive financial aid. Attending college full time may mean either taking 15 credits or 12 credits each semester, depending on the institution. It is highly recommended that students speak to a Financial Aid Advisor if they are dropping below full-time status to learn about how that impacts their financial aid.
Once students complete the FAFSA, and have been offered financial aid, they can subtract that amount from the total annual tuition cost to determine their out-of-pocket expenses.